
If you want to leave a more eco-friendly lifestyle, it takes a bit of effort to figure out the best recommendations for recycling at home. No one’s born knowing what recycling numbers mean. The universal recycling symbol features three arrows that form a triangle, but it’s the plastic’s number that makes a difference as to whether or not the item can head to your recycle bin. And although many plastics can be recycled, National Geographic reports that 91 percent of plastic has never been recycled. The World Economic Forum’s 2016 study found that 32 percent of plastic packaging ends up in our oceans every year. There’s no denying that plastic is a versatile material-it’s in everything from food utensils to toys-but too much of a good thing is also damaging the planet.
#Recycle numbers how to#
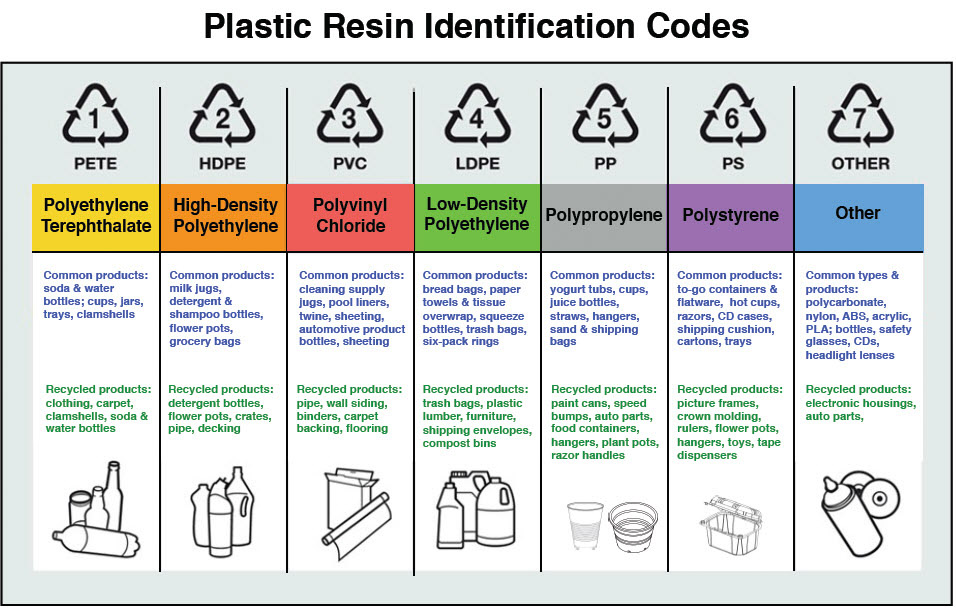
Can I actually recycle this? Which numbers are OK for my bin? And what do those numbers mean anyway? Today we’re answering your recycling questions, and shedding some light on how to decode the mystery numbers on certain packages, bottles, and containers. Until a truly sustainable plastic can be developed, reducing its role in our society will be far more impactful than any amount of recycling.You’re all ready to recycle and do your part for the environment, but then the questions start. If you’re able, consider supporting companies that minimize this environmental harm, as well as legislation that regulates plastic use. It’s also worth noting that individual consumers’ plastic consumption accounts for only a fraction of the waste across the globe: far more to blame are the corporations that make this material and use it wastefully for packaging, shipping, and manufacturing. Cloth bags, glass jars, cardboard boxes, and ceramic dishware are all examples of items we can use to replace plastic in our lives. The key to reducing that harm is avoiding plastic as much as you can-especially plastics designed to be disposable. No matter what you do with it, plastic hurts our planet’s ecosystems, atmosphere, and natural resources. You’ll need to do more research to determine where and how to dispose of it.Ĭreating plastic takes fossil fuels, recycling it produces greenhouse gasses, and throwing it away creates harmful waste. This means that you can’t just toss this type of plastic into a recycling bin or a compost pile and wait for it to dissolve. Moreover, “biodegradable” plastics often require special recycling facilities. While seeing this label may call to mind a gently rotting compost pile, degrading plastic items can be problematic: depending on their specific makeup, they may simply break down into microplastics, which end up in our soil, water, and food supply. “Biodegradable” plastic does just that: it degrades over time.
How do biodegradable and compostable plastics work? So while bioplastics have the distinct benefit of decreasing our reliance on fossil fuels, they often don’t spare the planet from harmful plastic waste. If you’ve been handed a piece of bioplastic, such as a to-go drink cup or a single-use bag, this level of diligence may not be possible. The only way to know for sure how to properly dispose of bioplastic items is to carefully read the labels on their packaging and research your local recycling policies. While some bioplastics can be recycled, they often have to be separated from petroleum-based plastics so they can be processed in a different way.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
